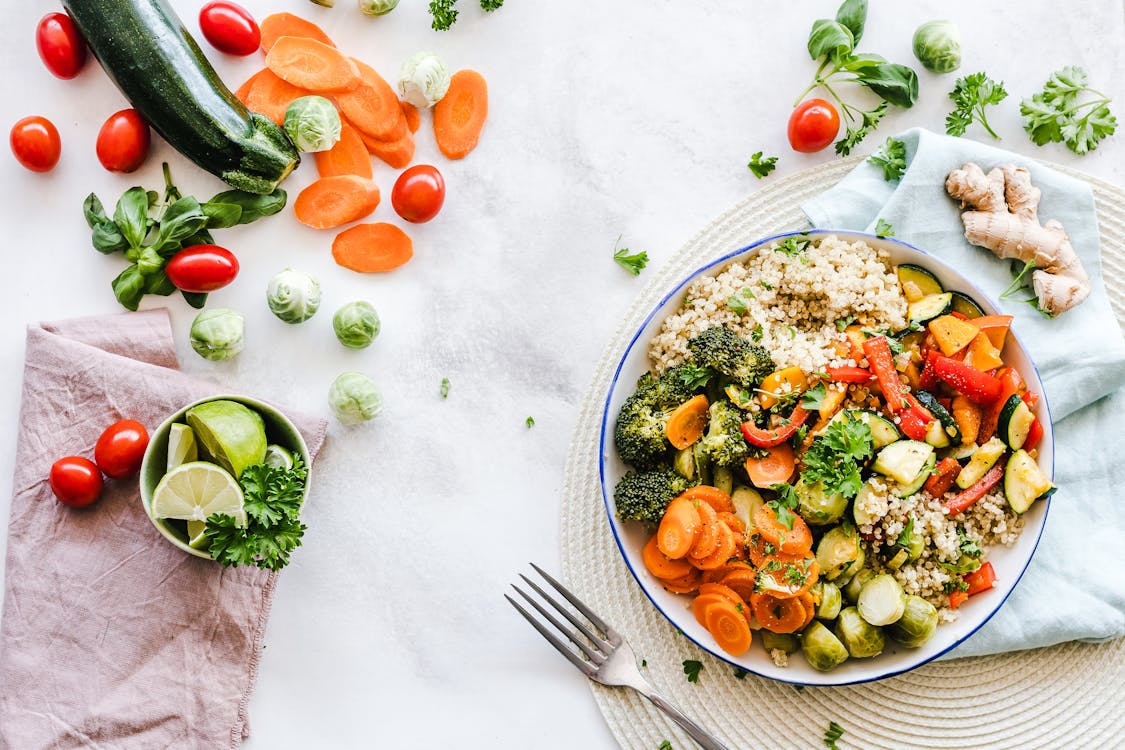
Your quick guide to eating healthier grains!

A grain of rice contains 3 layers – the germ (inner layer packed full of vitamins and minerals), the endosperm (middle layer of starchy carbohydrates), and the bran (outer layer full of fibre). White rice is processed, which means that the germ and bran layers are removed, leaving only the calorie-dense carbohydrate layer.
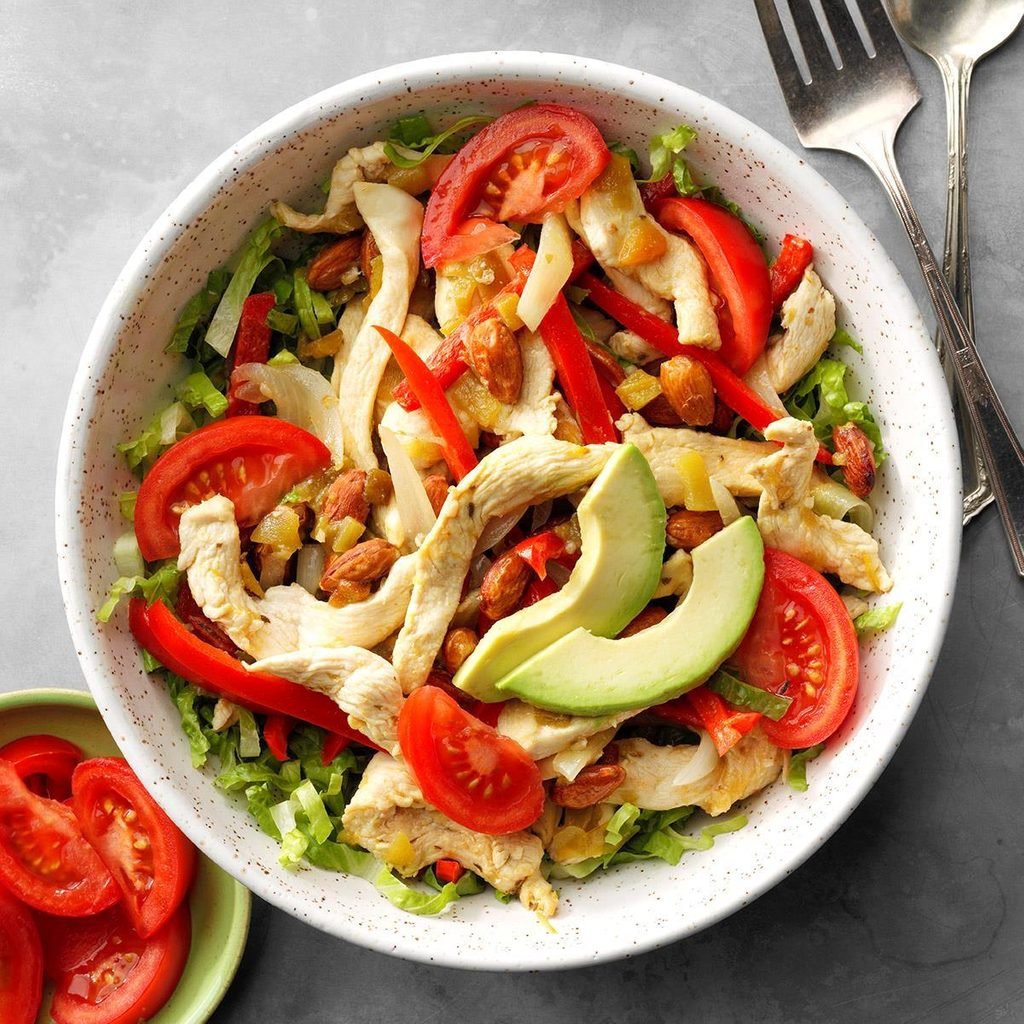
Consider the alternative options to white rice below. These options will assist in increasing your nutrition with additional vitamins and minerals and you will get more value out of the food you eat!
Brown rice contains all three grain layers, so it is full of fibre and healthy nutrients. Per 100 grams of cooked brown rice, you get 112 calories, 2.3 grams of protein, 1.8 grams of fibre (vs. 0.3 grams in white rice), while also providing 11% of your daily manganese intake, and 5% of your Vitamin B6 intake. Brown rice also contains many antioxidants, meaning it can help reduce the risk of developing many chronic health conditions such as heart disease and type 2 diabetes.
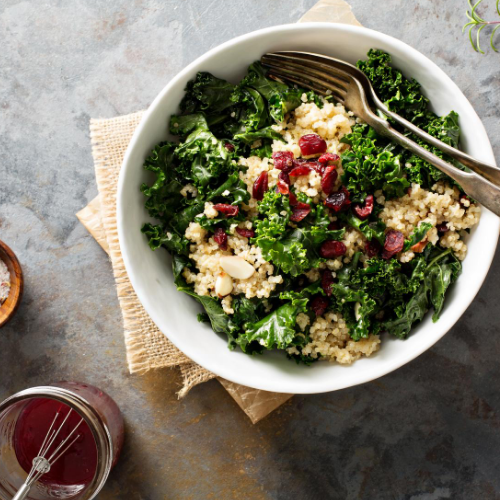
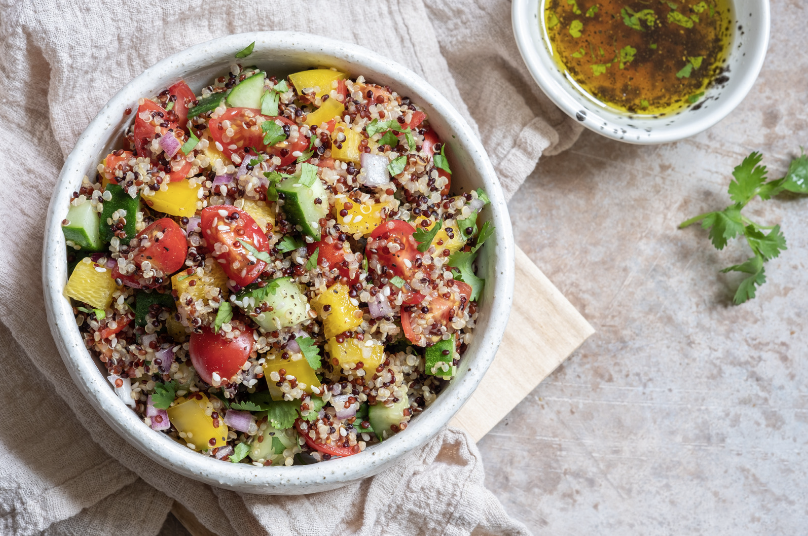
Quinoa is a type of seed that is rapidly growing in popularity as a grain alternative. Per 100 grams of cooked quinoa, you get 120 calories, 4.4 grams of protein, 2.8 grams of fibre, and it is a good source of manganese, phosphorus, folate, iron, magnesium, and zinc. Compared to white rice, this means that per serving, quinoa has double the protein and more fibre, vitamins, and minerals, which will help you feel “full” longer, with a more balanced energy level.
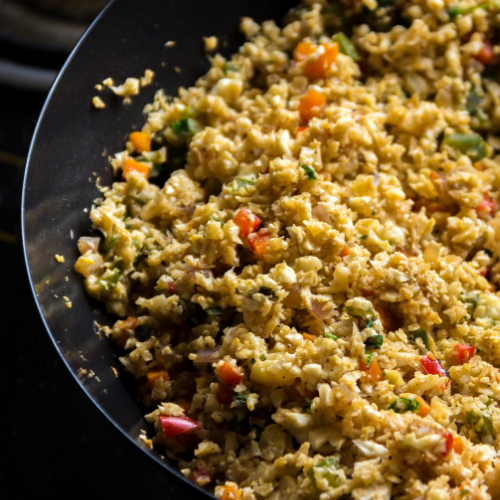
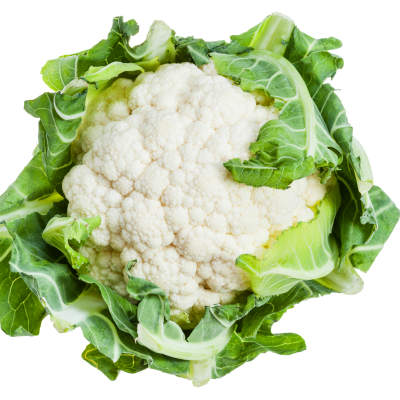
Cauliflower rice is another growing food trend that contains only 25 calories per cup of raw cauliflower yet is still packed full of vitamins and minerals. Per cup, it has 3 grams of fibre, 77% of your recommended daily intake of Vitamin C, 20% of your Vitamin K, 14% of your folate, 11% of your Vitamin B6, and smaller portions of potassium, manganese, magnesium, and phosphorus. The preparation method is also simple: put the cauliflower in a food processor (or buy ready-to-go packaged cauliflower rice), then replace it in any dish that you would normally eat white rice!
Bulgur is a whole grain cracked wheat that when cooked is similar in texture to couscous or quinoa. Per cup of cooked bulgur, you get 150 calories, 8 grams of fibre, 6 grams of protein, 14% of your daily recommended intake of magnesium, 10% of your Vitamin B6, and 9% of your iron. Bulgur is also very easy to cook and goes well with most recipes as a substitute for any kind of rice or couscous.