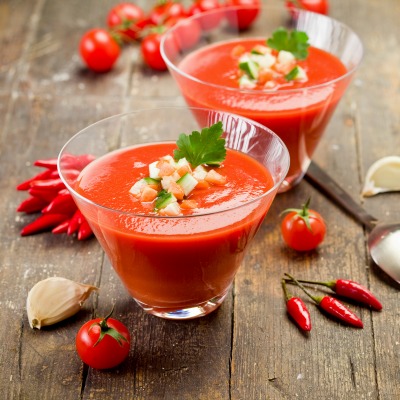
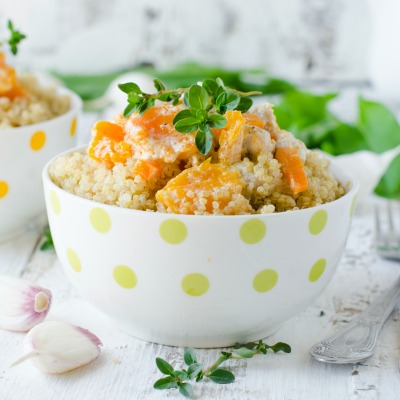
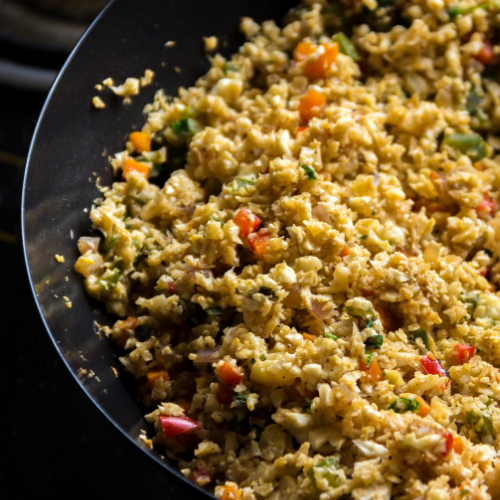
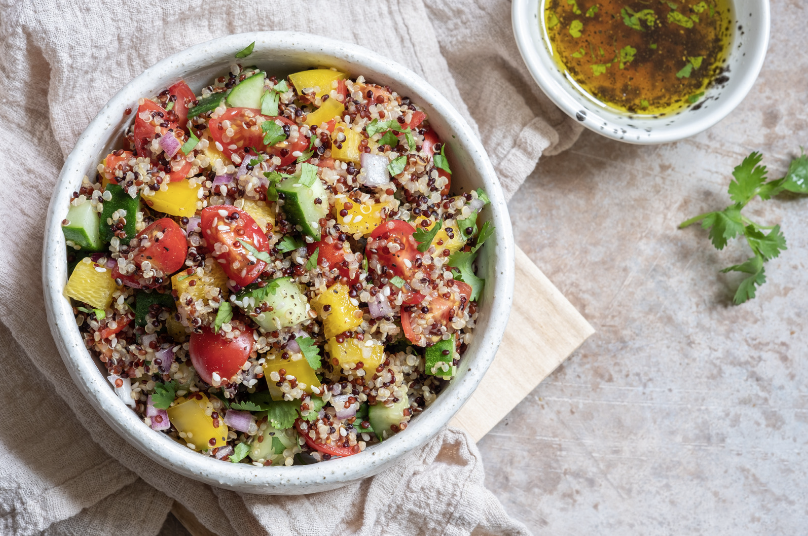
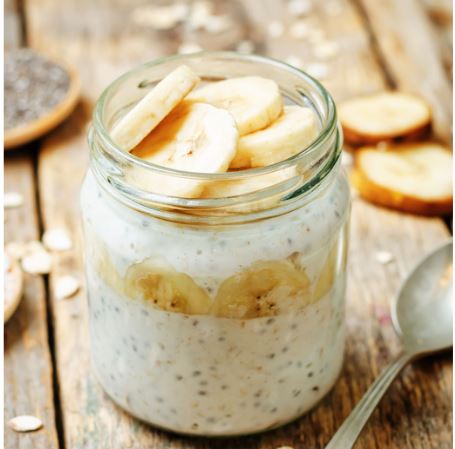
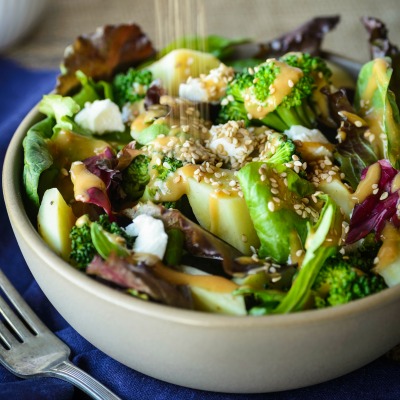
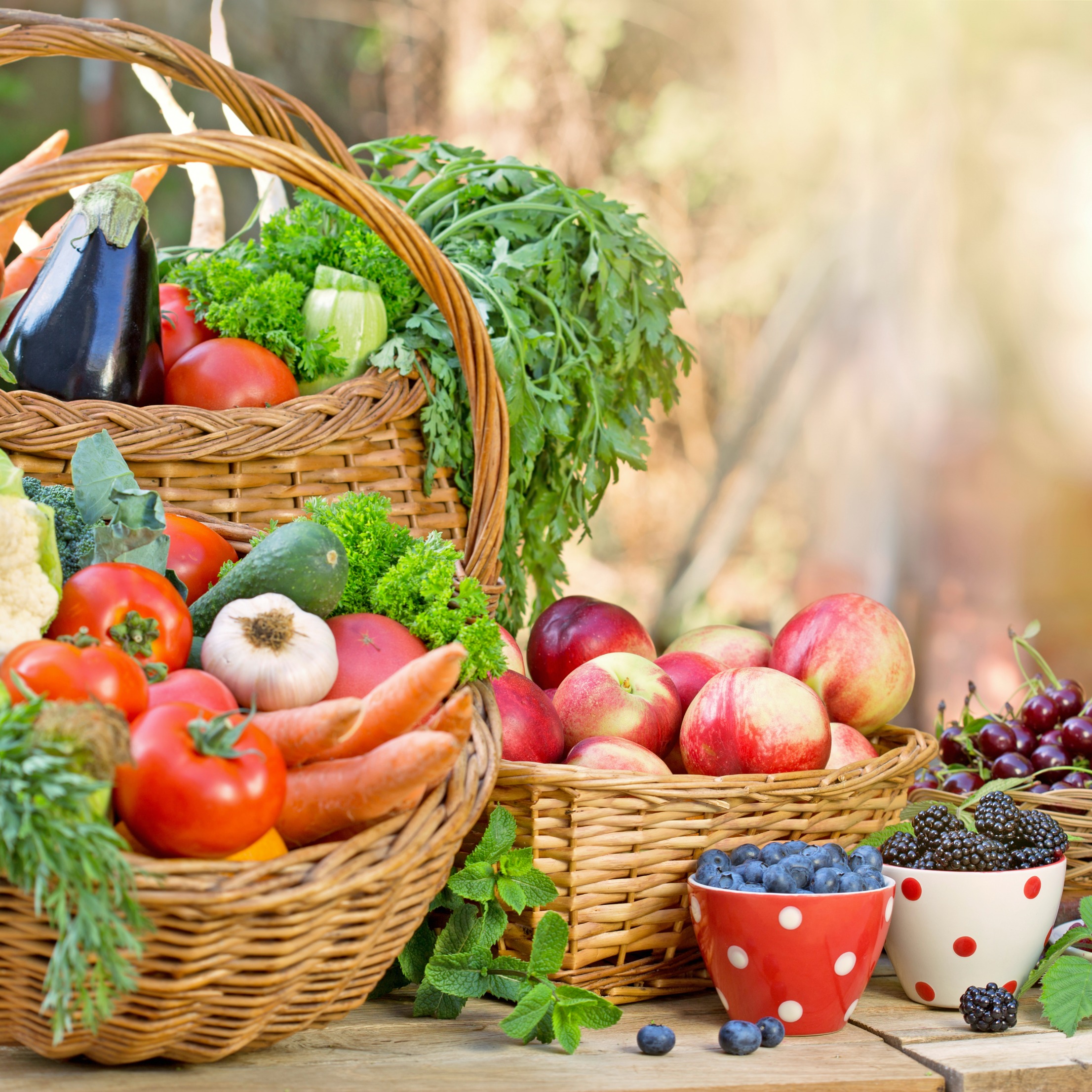
The raw food diet is based on the belief that the most healthful food for the body is food in its most natural state – uncooked and unprocessed.

Cooking is thought to denature (break apart) the enzymes naturally present in food, which are responsible for helping us to digest and absorb nutrients. The theory is if we eat too much cooked food, our bodies have to work harder to produce more enzymes. Over time, it is thought this can lead to digestive problems, nutrient deficiency, accelerated aging, and weight gain. The raw food diet is not a weight-loss plan, it is a lifestyle choice.
What is in a Raw Food Diet?
A raw food diet is typically made up of 75% fruits and vegetables. Staples of this diet include:
- Seaweed
- Sprouts
- Sprouted seeds
- Whole grains
- Beans
- Dried fruits
- Nuts
Most people who follow a raw food diet are vegan. Some consume raw animal products, such as raw milk, cheese made from raw milk, sashimi, ceviche (raw fish), or carpaccio (raw meat).
Health Benefits of the Raw Food Diet
There are studies that back up the premise that cooking vegetables tends to kill important nutrients. One research study showed that eating raw vegetables like cabbage, Brussels sprouts, broccoli, and kale may reduce the risk of bladder cancer. Another study found that raw vegetables help lower the risk of oral, pharyngeal, esophageal, and gastric cancers.
Health Concerns of the Raw Food Diet
Researchers have found that those who followed a raw food diet had a vitamin B12 deficiency, a vitamin found naturally in animal products that is crucial to nerve and red blood cell development. Another study found that those on a raw food diet had lower than average levels of plasma lycopene, which is thought to play a role in disease prevention. Lycopene is found in deep-red fruits like tomatoes, and is at its highest concentration when the tomato is cooked.
The Verdict
Although the raw food diet is rich in nutrients, full of fiber, and low in fat and sugars, it may leave you deficient in some important vitamins and nutrients. Vitamin B12, calcium, iron, and omega-3 fatty acids are a few examples – these are mostly found in animal products. If you choose the raw food diet, you must be careful that you are receiving the nutrition necessary to stay healthy.
The American Dietetic Association offers these guidelines:
- Consume 8 mg - 45 mg per day of iron – good sources include tofu, legumes, almonds, and cashews
- Eat at least 8 servings of calcium-rich foods – examples: bok choy, cabbage, soybeans, tempeh, and figs (goal: 1200 mg - 2000 mg per day of calcium)
- Eat fortified breakfast cereals, nutritional yeast, and fortified soy milk for vitamin B12 – consider taking supplements as well (need at least 2.4 mcg/day)
- Eat flaxseeds and walnuts, and use canola, flaxseed, walnut, and soybean oil – these are all sources of omega-3 fatty acids (500 mg - 1000 mg daily of EPA plus DHA)
Sources: WebMD - Raw Food Diet, About.com - Raw Food