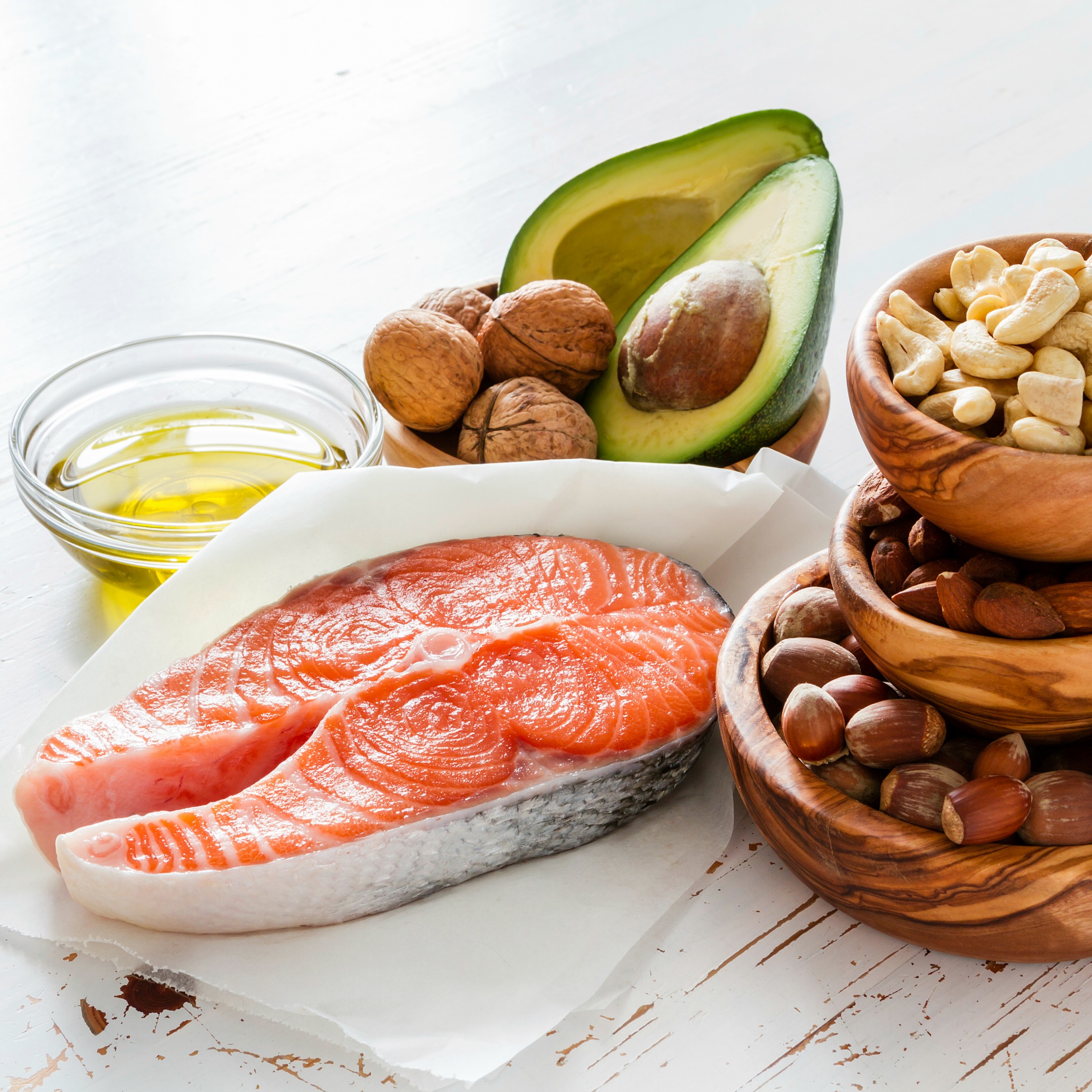
Fish oil is a great source of omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA and when eaten regularly may help with blood clotting, as well as reducing blood triglycerides and blood pressure.

Omega-3 Essential Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fats are essential fatty acids, which means that they are required to be in the diet for good health. Omega-3 is a term commonly used to refer to two kinds of omega-3 fatty acids: eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA).
Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) – another fatty acid that comes from plant foods such as flax seeds, chia seeds, seaweed, and walnuts – can also be used by the body to synthesize EPA and DHA, but in small amounts that vary unreliably between people.
The fatty acids EPA and DHA are essential to the diet because they are involved in regulating various biological functions like the inflammatory response, metabolic signaling, and brain function.
For the last few decades, there has been a common long-standing belief that eating more fish or taking omega-3 supplements reduces the risk of heart disease, stroke, and death.
However, the most up-to-date systematic reviews of accumulated scientific literature suggest that increasing EPA and DHA omega-3 intake has little or no effect on the risk of developing and/or dying from heart disease. There is also little evidence of effects from eating fish.
What is Fish Oil
The term “Fish Oil” refers to a type of oil typically found in, and often derived from fatty fish such as anchovy, salmon, mackerel, herring, and sardines. These oily fish naturally have the highest omega-3 content of up to 30% combined EPA/DHA.
The amount of omega-3 that a person needs will vary depending on factors such as diet, genetics, lifestyle, age, body composition, health condition(s), and the bioavailability of the omega-3 product.
There are no official daily intake recommendations for omega-3, although a generally agreed-upon minimum daily intake of 500mg EPA/DHA is frequently recommended. However, it is important to note that health benefits were achieved with a minimum intake range of 2000–3500mg EPA/DHA in scientific literature.
Known Benefits of Omega-3 Supplements
Research indicates that omega-3 supplements do not reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke. However, there is evidence for various other reliable health benefits of omega-3 fatty acids:
- High doses of omega-3 (+2000mg EPA/DHA) can reduce levels of triglycerides in the blood.
- Omega-3 supplements may help relieve symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis.
- It appears to notably improve mood and anxiety in people with major depression, though it is unclear if it has an effect in people with minor depression.
- Omega-3 supplements have not demonstrated the ability to slow the progression of the eye disease age-related macular degeneration as previously thought.
- For most other conditions for which omega-3 supplements have been studied, the evidence is inconclusive or does not indicate that omega-3s are beneficial.
Are You Getting Enough Omega-3s?
Many omega-3 supplements contain very low omega-3 doses, and most fish oil capsules will have an advertised content of ~1000mg of fish oil. However, since natural fish oils typically contain just 30% EPA/DHA combined, that leaves only 300mg of available EPA/DHA per 1000mg capsule of fish oil.
At a small dose of 300mg, you would need to take up to 7 regular fish oil capsules just to reach the 2000mg EPA/DHA for minimum known benefits. (300mg x 7 capsules = ~2100mg EPA/DHA)
The best way to know how much omega-3 is available in your fish oil supplement is to look at the EPA and DHA content listed on the nutrition label. The quality of omega-3 fish oil products will vary depending on the brand, source, and freshness of the oil.
Refer to the table below for an estimated comparison of the number of servings needed to get 2000-3500mg EPA/DHA for typical omega-3 supplements.
| Product Type | EPA/DHA per serving | Servings needed to get 2000mg-3500mg EPA/DHA |
|---|---|---|
| Regular Dose Fish Oil Capsule | ~300mg EPA/DHA | 7-10 capsules |
| High Dose Fish Oil Capsule | ~600mg EPA/DHA | 3-5 capsules |
| Krill Oil Capsule | ~75mg EPA/DHA | 27-40 capsules |
| Cod Liver Oil Teaspoon | ~1000mg EPA/DHA | 2-3 teaspoons |
| Wild Salmon Fillet (6oz) | ~2000mg EPA/DHA | 1 fillet (6oz) |