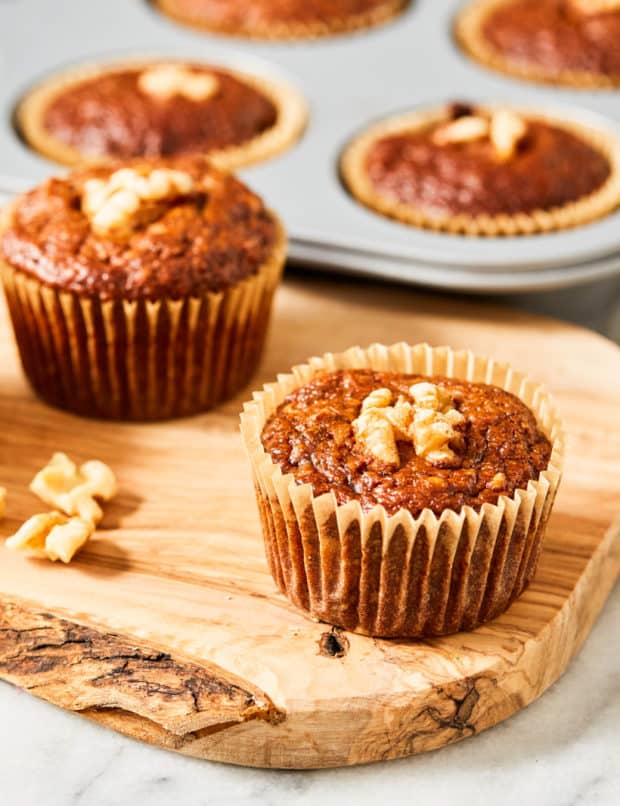
What are the differences between Honey and White Sugar?
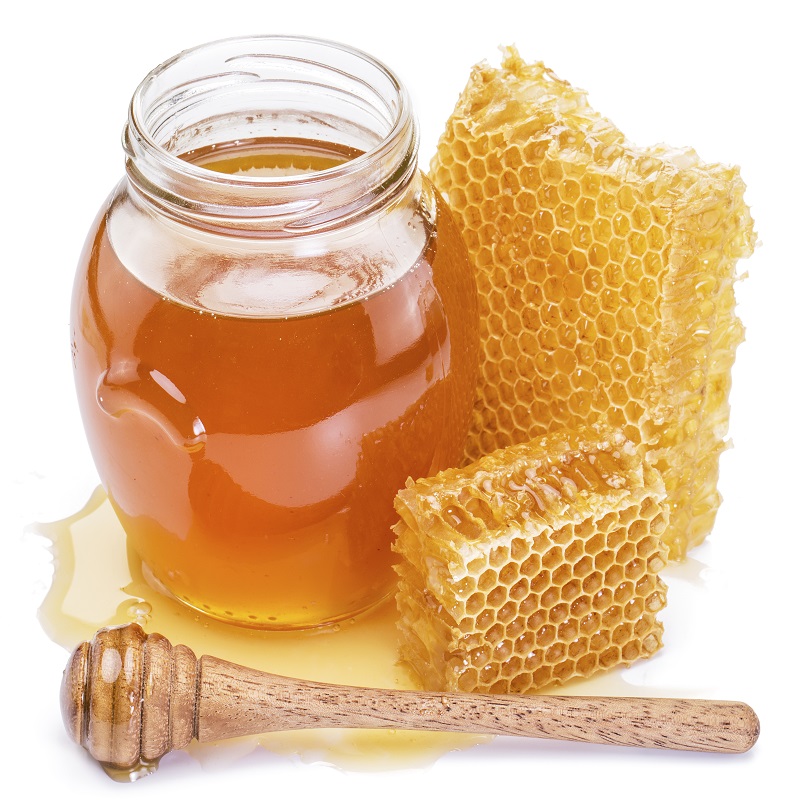
Honey and white sugar are both sources of carbohydrates and are made up of sugar molecules. Honey is comprised of mainly fructose and glucose sugar molecules and tastes sweeter than white sugar. Honey also contains some vitamins and minerals. White sugar on the other hand is lower in calories than honey and is comprised solely of the sugar molecule sucrose.
Honey: 1 tbsp (15ml/21g) = 65kcal, 17.6g Carbohydrate
White Sugar: 1 tbsp (15ml/13g) = 49kcal, 12.6g Carbohydrate
Honey also has anti-inflammatory properties, contains vitamins and minerals, boosts your immune system, and contains antioxidants!
Although honey is higher in calories and carbohydrates than traditional white sugar (per tablespoon), honey is lower on the Glycemic Index and you can use less of it as it tastes sweeter!
What is the Glycemic Index (GI)?
The Glycemic Index is a tool used to rank carbohydrates on how they affect blood sugar levels. Your body converts starches and complex sugars from the foods you eat into simple glucose, and the glucose is used for energy to fuel your body. The GI number given to foods and beverages indicates how quickly your body metabolizes them into glucose, and how quickly the glucose is released into your blood stream. Foods and beverages with a high GI number (70 +) raise your blood glucose levels faster and higher than foods and beverages which rank lower on the GI scale (55 or lower).
For example, if a food has a GI of 75, it is metabolized more quickly and is released into your bloodstream more quickly, which can raise your blood glucose levels more drastically than a food that has a GI of 45.