January is Alzheimer's Awareness Month. Did you know Alzheimer's disease is the most common form of dementia? There are several different types of dementia that researchers are still working to better understand. Although there is currently no cure for dementia, treatments have been shown to slow disease progression.
To better understand dementia, let's first talk about brain health.
What is Brain Health?
• Brain health refers to how well the different parts of the brain function:
- Cognitive function: How well you think, learn, and remember.
- Motor function: How well you balance and move.
- Emotional function: How well you understand and react to emotions.
Brain health declines naturally as we age. Lifestyle choices and disease(s) can increase this decline.
What is Dementia?
• Dementia is a term used to describe several conditions that affect how the brain works.
- It is a chronic condition that gets worse and more severe over time.
- Dementia can lead to loss of memory, inability to talk, and inability to judge/plan.
- It is primarily seen in adults older than 65, but young-onset dementia also exists.
There are currently six different types of dementia:
- Alzheimer's disease: This is the most common type, making up 60-70% of all dementia cases.
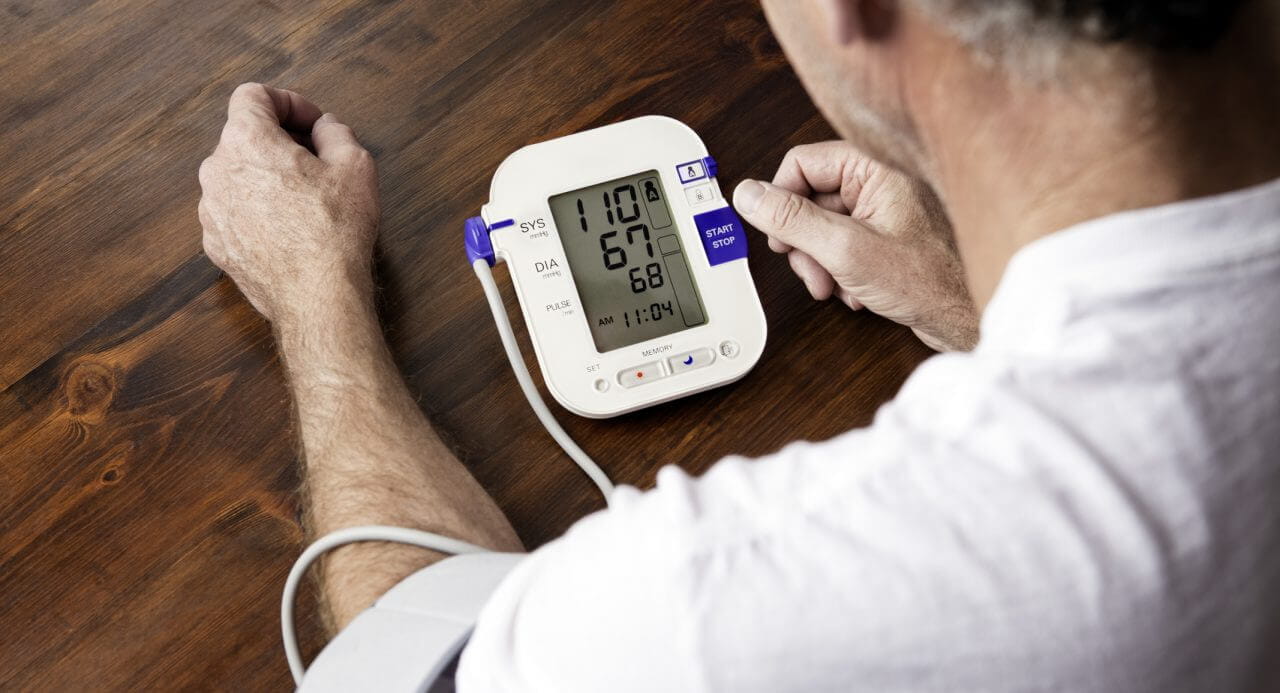
- Vascular dementia: This happens when the brain does not get enough blood. Strokes and/or high blood pressure can cause it.
- Lewy body disease: Abnormal proteins in the brain cause problems with thinking and movement (like shaking or slow movements).
- Mixed dementia: This is when someone has two types of dementia, often Alzheimer's disease and vascular dementia together.
- Frontotemporal dementia: This affects the parts of the brain that control behaviour, personality, movement, and speech.
- Korsakoff dementia: This is caused by a lack of vitamin B1, often due to heavy alcohol use or poor diet.